Introduction
“Because the purpose of business is to create a customer, the business enterprise has two-and only two-basic functions: marketing and innovation. Marketing and innovation produce results; all the rest are costs. Marketing is the distinguishing, unique function of the business.”[1]
Why marketing? Because it is important for companies to fully understand consumer’s behaviour whether they are a person or an institutional buyer.
When we talk about the buyer’s behaviour is it good to understand how they decide? why do they prefer one place over another? How does increased access to information affect purchasing and spending choices? Delloitte’s answer refers, for example, to the three R’s – research, recommendations and returns – which may hold the key to consumer understanding.
Research
If we talk about research – it is based on digital technology that provides an unprecedented level of information. Here we can talk about influencers who may be completely unknown people but who can influence the purchase decision.
Recommendations and reviews
Recommendations and reviews on products, goods, services are increasingly sought after in the design of purchasing decisions.
Consumers are looking to gather information from
– Expert reviews
– User opinions
According to the EUROPE E-COMMERCE REPORT 2021 Customer reviews are, for an “important source of feedback, a trust enhancing mechanism, and a source of information for (potential) customers.
Within EU,
- 59% of e-stores offer customers the opportunity to write
- product reviews, and
- 23% provide consumers the option to review the company itself.
Returns
The possibility of return is an element that encourages the consumer to buy because one knows that within a certain time, they can return the product without penalty or with a small penalty. In this case, remorse, dissatisfaction, poor evaluation of the product before purchase are good reasons for returns.
The aim of this chapter is to understand the consumer behaviour as an important issue for effective marketing, helping managers to make selling decisions.
Learning objectives:
- To place consumption in the context of human behaviour
- To identify consumer behaviour in the context of the evolution of the online shopping and social shopping
Buyer, customer, or consumer are three almost similar expressions and are treated as such:
Buyer[2] – a person who has charge of the selection, purchasing, pricing, and display of the merchandise of a retail store
Customer[3] – a person who buys a product or uses a service from a business
Consumer[4] – a person who buys goods and services
What do these people have in common:
Search for:
– Sources of product information?
-Ways to evaluate alternative products (opinions, reviews, social media, influencers)
– Information about other users (experiences)
It is informed / analysed:
– What is the value for money of the product
– What are the risks of purchasing the product / service
– What influences the purchase decision?
On the other hand, B2C aim to find out:
– Who / what influences the decision to buy or use a product
– How is brand loyalty formed and changed?
– What are the internal factors that affect the purchase decision (psychological, personal, social)
To summarise, a typical definition of consumer behaviour might be the following:
- The mental, emotional and physical activities that people engage in when selecting, purchasing, using and disposing of products and services so as to satisfy needs and desires.[5]
According to Eurostat[6] 74 % of internet users in the EU shopped online in 2021 and 42 % of e-buyers made purchases for an amount between 100 to less than €500 in the last 3 months prior to the Eurostat survey.
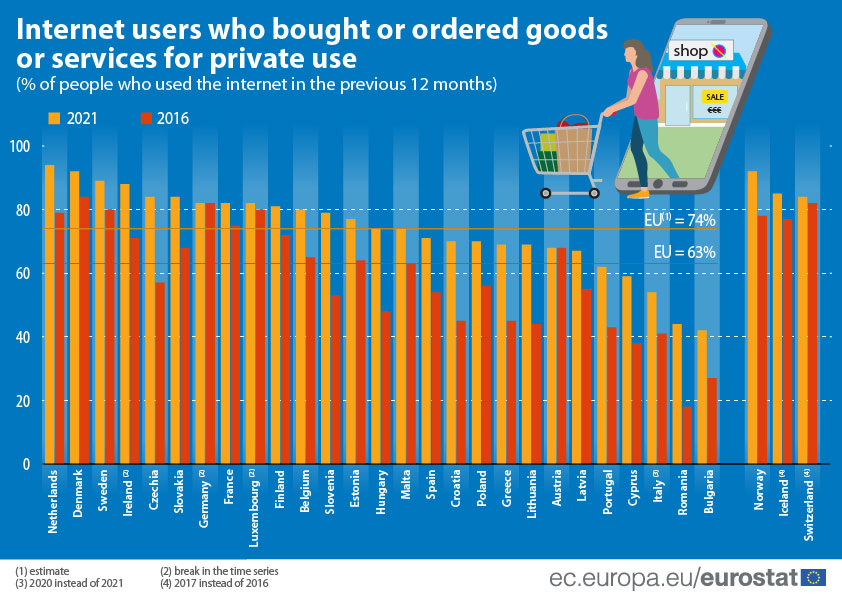
Consumer behaviour types
We all are consumers hence consumer behaviour is an integral part of our daily lives. But we are not all the same and psychological and social processes involved in buying and consuming goods and services make the difference.
The literature recognizes four types of consumer behaviour:
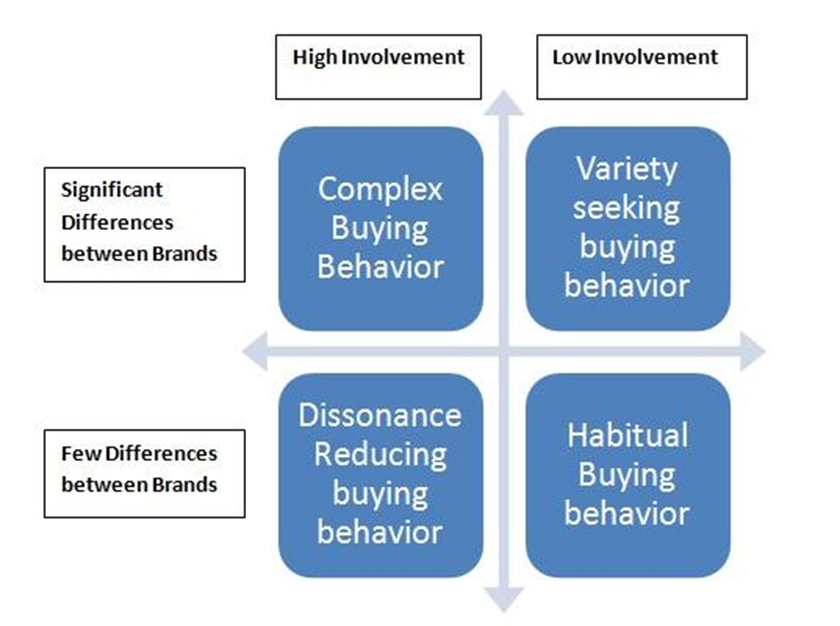
Figure 3 Source: https://clootrack.com/knowledge_base/types-of-consumer-behavior/
- Complex buying behaviour – Buying something very expensive such as a house or a fancy car. People in this situation
- make in depth research before the purchase decision,
- look for advice (family, friends, specialists)
- inform themselves from multiple sources,
- search online for the market offer and look for alternatives, pros, and cons
- Dissonance-reducing buying behaviour – buying infrequent a good or a service. Because of a low availability of choices with less significance differences among brands and prices, consumer do not have many choices and lot of research is not necessary for purchase decision.
Some characteristics:
- Infrequent purchases
- Low availability of choices
- Limited decision making
- Time limitations
- Budget limitations
- Habitual buying behaviour – is daily buying for each customer. It does not include too much thinking it is more about the attitude.
For example, while a consumer buy bottled water, he always tends to buy the familiar brand without a lot of research and time investment. He knows the product and like it.
- Variety seeking buying behaviour
The buyer from this category enjoys changing own buying decision as there is plenty of brands on the market and there are low costs to make the decision.
For example, the consumer buys a certain bottled water one day and change it next day to try something new.
More about consumer behaviour types you can have a look to the YouTube: Steven Fob[7] – Four Types of Buying Behaviour https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bnrdv-7ndFo
What is social shopping?
Well, social shopping can be seen as an adventure of buying things combining e-commerce with social media, allowing people to buy directly on different platforms like Facebook, Instagram and Tik Tok.
The importance of social shopping is a two-way road. One the one hand there is a huge consumer bases that can buy easy via social media platforms and on the other hand companies can put their storefront directly on the platforms.
According to the 2021 European E-commerce Report[8] :
- 93% of the European web shops display their social media channels on their website
- The most popular media channels used by online stores are Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube
- Less frequently used social media platforms are Tumblr, Snapchat and
TikTok.
- Web shops from Northern Europe have fewer Pinterest (8%), YouTube (55%) and Instagram (69%) accounts on their website.
- Additionally, Twitter is much more popular among e-stores in Western Europe (71%) and Southern Europe (53%), compared to Northern Europe (24%) and Eastern Europe (26%)
According to the same report the most preferred use of contact options in EU 27 are:
- Phone call = 90%
- E-mail = 74%
- Contact form = 66%
- Chat = 47%
- Instant messaging/VOIP = 11%
- Fax = 8%
Knowing the preferred contact options of consumers help web shops to design proper communication channels to rich consumers.

Figure 4 Source: EUROPE E-COMMERCE REPORT 2021
All these information shows that selling through social media channels is onnected to disruptive B2B, and B2C techniques.
Starting from the 5 Stages of the Consumer Decision-Making Process[9], let’s see how they changed.
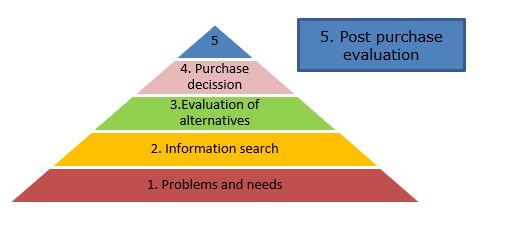
- Need identification – is the point at which the consumer identifies the problem, need or desire. It is an area quite little used by companies that, at this moment, could create the need and use every channel to get customers to their products. The need identified is linked very close to the point 5 post purchase evaluation.
Moreover, for the B2B or B2C it is strongly important to answer two questions:
- What problem your product or service solve?
- Is it easy enough for customers to find your brand using normal search engines?
Example: You are a knitting accessories vendor, and COVID 19th kept people in the house. So many people have tried to spend their time with various hobbies, one of them being knitting. So, in a simple search it appears, and obviously many more
In our case, the first three that appeared are: Alibaba, Made in China, Amazon.de
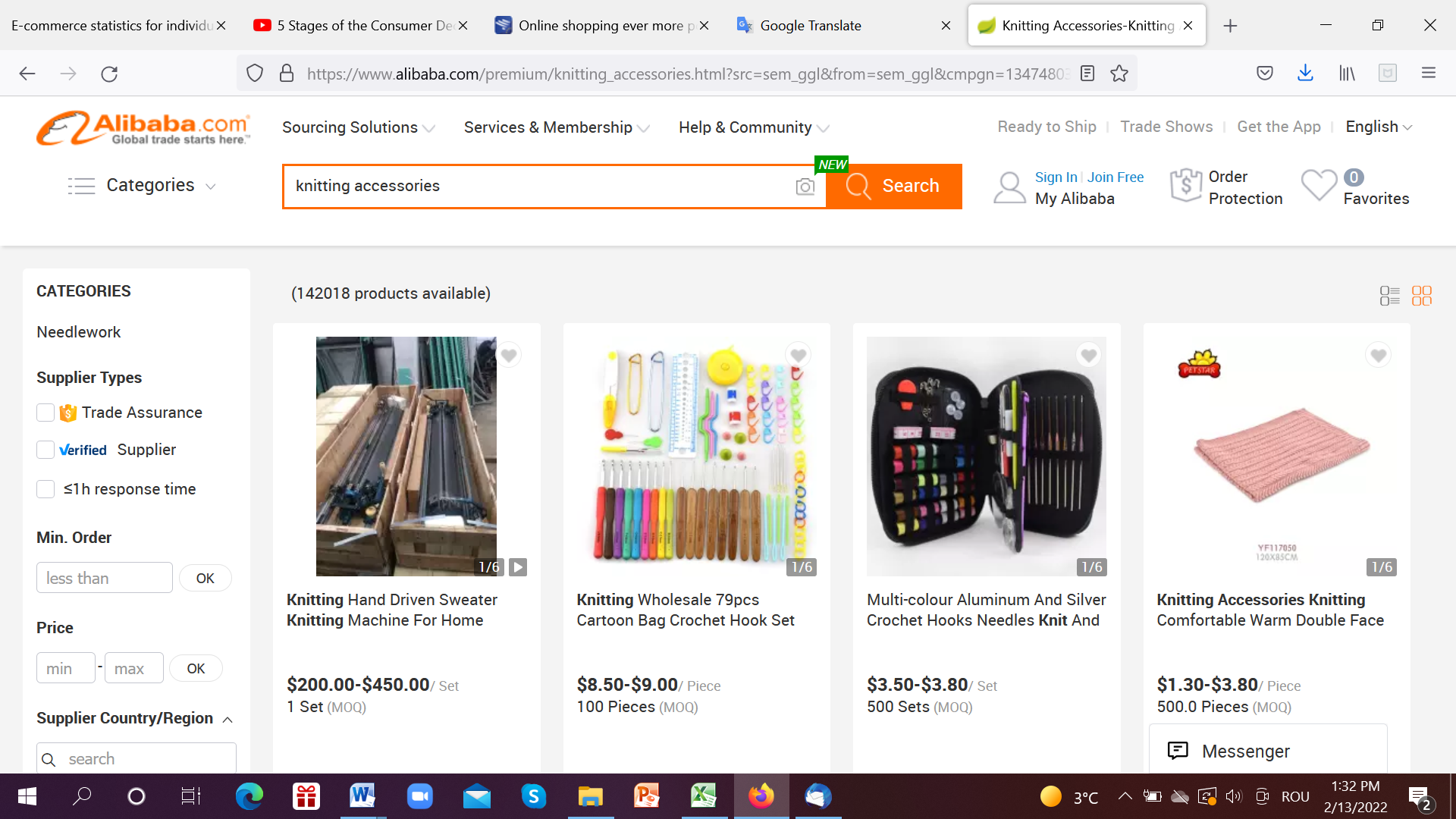
Figure 5 Website visited 13.02.2022
- Information search – years ago, buyers did not have many sources of information about certain products or services they needed. Therefore, they used family and relatives as a resource, newspapers, TV networks, and a daddy. Today, the multitude of information around us is possible thanks to the Internet, electronic applications, social networks, and much more. For B2C it is a great opportunity and a need to provide information that helps potential customers get informed.
The question buyers want to answer to is, If I need a product from which place will I buy it, who will offer me what I need?
For B2C and B2B is very important to answer this question. If they manage to do so, here is the point where the revenue is coming for the company.
- Evaluation of alternatives – people are very interested to find and buy the best from the alternatives they have. At this point they will not look to your website, your apps, but they will check against other people recommendations and reviews. The research companies are providing information to customers and companies need to be part of this process because you do not control anymore what other people think about your product, but other people control that.
- The purchase decision – having in mind consumer behaviour that is different based on buyer models. Here some examples:
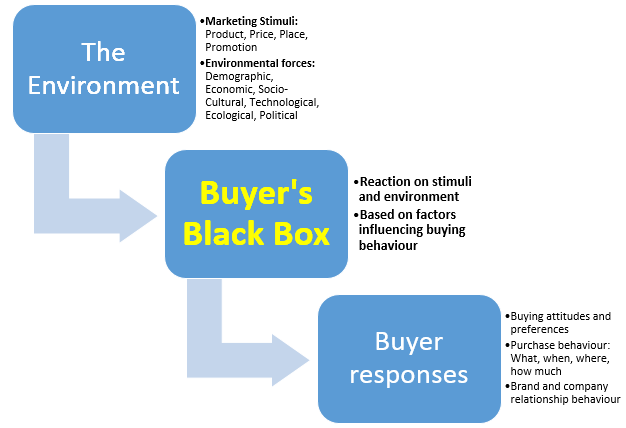
Figure 6 Source: https://marketing-insider.eu/buyer-black-box/
The buyer`s decision is influenced by cultural, social, psychological factors that cannot be easy influenced but B2B or B2C need to know them.
They are:
| Cultural factors | Social | Personal | Psychological |
| Culture
Subculture Social class |
Social networks
Small groups Family Role & status |
Age and lifetime stage
Occupation Economic situation |
Motivation
Perception Learning, memory and thinking Beliefs& attitude |
Figure 7 Source: Marketing Insider, 2019 https://marketing-insider.eu/buyer-black-box/
- Post purchase evaluation – when speaking about purchase evaluation, as always, not all customers are happy with the goods or services bought. Return possibility encourage buying. At this stage B2B and B2C need to gather as much feedback as possible to realize what is wrong and to improve the situation.
[1] https://www.forbes.com/2006/06/30/jack-trout-on-marketing-cx_jt_0703drucker.html?sh=431fad76555c visit 06.02.2022
[2] “Buyer.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/buyer. Accessed 7 Feb. 2022.
[3] “Customer.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/customer. Accessed 7 Feb. 2022.
[4] “Consumer.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/consumer. Accessed 7 Feb. 2022.
[5] Edinburgh Business School – Consumer Behaviour Jane Priest, Stephen Carter, David A. Statt
[6] https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=E-commerce_statistics_for_individuals#General_overview
[7] Steven Hob Four Types of Buying Behaviour https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bnrdv-7ndFo visited 13.02.2022
[8] https://ecommerce-europe.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/2021-European-E-commerce-Report-LIGHT-VERSION.pdf
[9] 5 Stages of the Consumer Decision-Making Process and How it’s Changed https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a9lpVg54u-k

 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Polski
Polski Română
Română Slovenščina
Slovenščina